Search Results for: anaerobic process
Anaerobic respiration
Anaerobic Respiration Definition What is anaerobic respiration? Anaerobic (cellular) respiration is a respiratory process... Read More
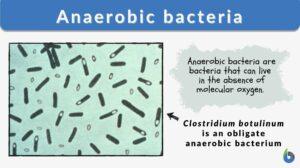
Anaerobic bacteria
Bacteria are classified according to the need for oxygen to survive and grow. For example, aerobic bacteria are bacteria... Read More
Fermentation
Fermentation Definition What is fermentation? Fermentation is the breaking down of sugar molecules into simpler compounds... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Facultative anaerobe
Facultative Anaerobe Definition What does facultative anaerobe mean? Facultative organisms are the most adaptable... Read More
Anaerobic process
Definition noun A (part of a) process that occurs in the absence of free oxygen. Supplement Examples of anaerobic processes... Read More
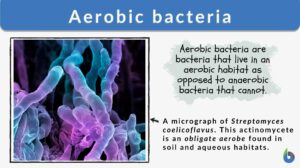
Aerobic bacteria
Aerobic Bacteria Definition What does aerobic mean in biology? As the name suggests, 'aerobe' in biology means organisms... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Obligate aerobe
Before we define obligate aerobes, let us first understand and define aerobic organisms. Aerobic organisms are those that... Read More
Catabolism
Catabolism Definition Catabolism is the branch of the metabolic process that breaks down complex, big molecules into... Read More
Aerobic process
Definition noun, plural: aerobic processes A process that occurs and requires the presence of oxygen or air Supplement An... Read More
Carbohydrate
Carbohydrate Definition A biomolecule refers to any molecule that is produced by living organisms. As such, most of them... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
Carbon fixation
Carbon Fixation Definition We know that the earth contains many elements. The periodic table shows us just how many... Read More
Aerotolerant
Aerotolerant Definition The term "aerotolerant" pertains to an organism that does not require oxygen for growth but can... Read More
Great Oxygenation Event
Great Oxygenation Event Definition The Great Oxygenation Event is defined as the surge of dioxygen (O2) levels in the... Read More
Eubacteria
Eubacteria are prokaryotic microorganisms consisting of a single cell lacking a nucleus and containing DNA is a single... Read More
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharide Definition Biology Definition: A polysaccharide is a carbohydrate formed by long chains of repeating units... Read More
Muscular system
Muscular System Definition What is the muscular system? The muscular system is a system that includes muscle cells and... Read More
Lactic acid
Definition noun (1) A colorless or yellowish, syrupy, water-soluble liquid, which is a byproduct of anaerobic glucose... Read More
Cell Respiration
As mentioned in the previous tutorial on ATP, the process of respiration is split into 3 distinct areas that occur at... Read More
Protein Activity and Cellular Metabolism
Protein Binding Sites The ability of various molecules and ions to bind to specific sites on the protein surface forms the... Read More
Biotic factor
Biotic Factor Definition A biotic factor is the living component in an ecosystem. The term "biotic" means "of or related... Read More
Monosaccharide
Monosaccharide Definition In biology and biochemistry, a monosaccharide is a simple sugar that constitutes the building... Read More
Chemiosmosis
Chemiosmosis Definition What is chemiosmosis? In biology, chemiosmosis refers to the process of moving ions (e.g. protons)... Read More
Pyruvic acid
What is Pyruvic Acid? Pyruvic acid is an organic acid that occurs as an intermediate in many metabolic processes. It occurs... Read More
Pasteur effect
Definition noun The inhibiting effect of oxygen on the fermentation process. Supplement The effect was discovered in 1857 by... Read More
Prokaryote
Prokaryote refers to any of the group of living organisms primarily characterized by the lack of a true nucleus and other... Read More
Aerobic respiration
Definition noun (1) A form of cellular respiration that requires oxygen in order to generate energy. (2) The process of... Read More
Unicellular
Unicellular organisms are organisms consisting of one cell only that performs all vital functions including metabolism,... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
Oligosaccharide
Carbohydrates are organic compounds consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, usually in the ratio of 1:2:1. They are one... Read More